By Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News
Results of a largescale collaborative project led by scientists at the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, and the University of California, Irvine (UCI), were published in the journal Neuron this week “Large-scale differentiation of iPSC-derived motor neurons from ALS and control subjects.”
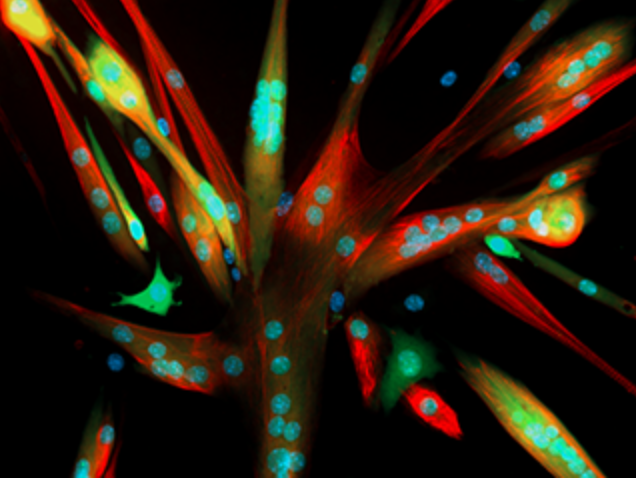
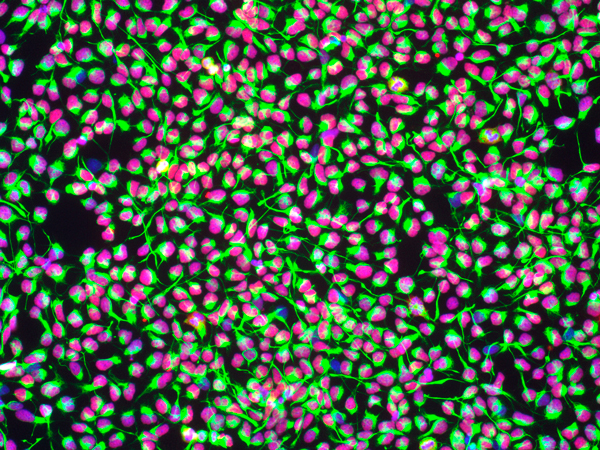
The study has generated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from 341 ALS patients and 92 healthy subjects, differentiated these into motor neurons, and profiled the differentiated cells using immunocytochemistry and RNA-seq. Profiling has revealed that the sex of the patient and cell culture composition are among the strongest drivers of gene expression variation in the iPSC-derived motor neurons, regardless of whether they were from patients diagnosed with ALS. Multiomic and clinical data available for the motor neuron samples in the repository, can potentially lead to the development of new ALS therapeutics that target specific cells and pathways.
The samples are available to the research community through the Cedars-Sinai iPSC Core and Biomanufacturing Center, led by Dhruv Sareen, PhD, executive director of the Cedars-Sinai Biomanufacturing Center, associate professor of Biomedical Sciences, and co-corresponding author of the study.