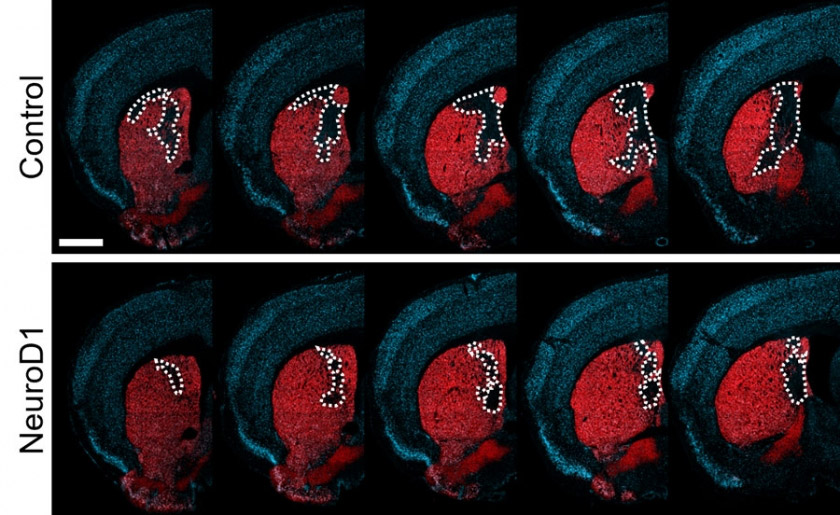
Fukuoka, Japan – Researchers at Kyushu University have discovered that turning brain immune cells into neurons successfully restores brain function after stroke-like injury in mice. These findings, published on October 10 in PNAS, suggest that replenishing neurons from immune cells could be a promising avenue for treating stroke in humans.
Stroke, and other cerebrovascular diseases, occur when blood flow to the brain is affected, causing damage to neurons. Recovery is often poor, with patients suffering from severe physical disabilities and cognitive problems. Worldwide, it’s one of the most common causes for needing long-term care.