By – Nature –
Despite treatment advances, multiple myeloma (MM) remains incurable1. High-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is considered the standard treatment for eligible patients2,3. Moreover, ASCT is reportedly effective and safe in older adults, thus expanding its applicability4. Novel agents have also been found to improve clinical outcomes in transplant-eligible and -ineligible patients.
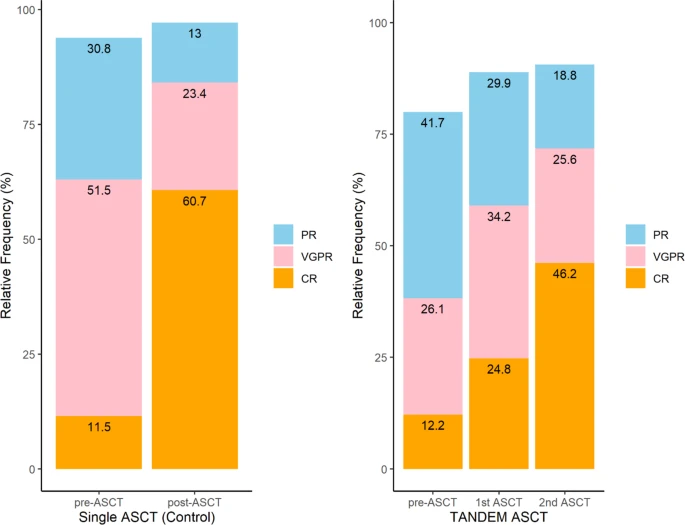
Tandem transplantation was proposed in the late 1980s to improve the prognosis of patients with MM and involves sequential transplantation. However, the results of several studies conducted to evaluate the clinical benefits of tandem transplantation are contradictory.